Summary of product characteristics
Adverse Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label: Increased Mortality, Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, and Thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] Increased mortality and/or increased risk of tumor progression or recurrence in Patients With Cancer [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2 )] Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3 )] Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4 )] PRCA [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6 )] Serious allergic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7 )] Severe Cutaneous Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.8 )] Patients with CKD: Adverse reactions in ≥ 5% of Epogen-treated patients in clinical studies were hypertension, arthralgia, muscle spasm, pyrexia, dizziness, medical device malfunction, vascular occlusion, and upper respiratory tract infection ( 6.1 ). Patients on Zidovudine due to HIV-infection: Adverse reactions in ≥ 5% of Epogen-treated patients in clinical studies were pyrexia, cough, rash, and injection site irritation ( 6.1 ). Patients with Cancer on Chemotherapy: Adverse reactions in ≥ 5% of Epogen-treated patients in clinical studies were nausea, vomiting, myalgia, arthralgia, stomatitis, cough, weight decrease, leukopenia, bone pain, rash, hyperglycemia, insomnia, headache, depression, dysphagia, hypokalemia, and thrombosis ( 6.1 ). Surgery Patients: Adverse reactions in ≥ 5% of Epogen-treated patients in clinical studies were nausea, vomiting, pruritus, headache, injection site pain, chills, deep vein thrombosis, cough, and hypertension ( 6.1 ). To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amgen Medical Information at 1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. 6.1 Clinical Trial Experience Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of other drugs and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Adult Patients Three double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, including 244 patients with CKD on dialysis, were used to identify the adverse reactions to Epogen. In these studies, the mean age of patients was 48 years (range: 20 to 80 years). One hundred and thirty-three (55%) patients were men. The racial distribution was as follows: 177 (73%) patients were white, 48 (20%) patients were black, 4 (2%) patients were Asian, 12 (5%) patients were other, and racial information was missing for 3 (1%) patients. Two double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, including 210 patients with CKD not on dialysis, were used to identify the adverse reactions to Epogen. In these studies, the mean age of patients was 57 years (range: 24 to 79 years). One hundred and twenty-one (58%) patients were men. The racial distribution was as follows: 164 (78%) patients were white, 38 (18%) patients were black, 3 (1%) patients were Asian, 3 (1%) patients were other, and racial information was missing for 2 (1%) patients. The adverse reactions with a reported incidence of ≥ 5% in Epogen-treated patients and that occurred at a ≥ 1% higher frequency than in placebo-treated patients are shown in the table below: Table 3. Adverse Reactions in Patients With CKD on Dialysis Adverse Reaction Epogen -treated Patients (n = 148 ) Placebo- t reated Patients (n = 96 ) Hypertension 27.7% 12.5% Arthralgia 16.2% 3.1% Muscle spasm 7.4% 6.3% Pyrexia 10.1% 8.3% Dizziness 9.5% 8.3% Medical Device Malfunction (artificial kidney clotting during dialysis) 8.1% 4.2% Vascular Occlusion (vascular access thrombosis) 8.1% 2.1% Upper respiratory tract infection 6.8% 5.2% An additional serious adverse reaction that occurred in less than 5% of epoetin alfa-treated dialysis patients and greater than placebo was thrombosis (2.7% Epogen and 1% placebo) [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )]. The adverse reactions with a reported incidence of ≥ 5% in Epogen-treated patients and that occurred at a ≥ 1% higher frequency than in placebo-treated patients are shown in the table below: Table 4. Adverse Reactions in Patients With CKD Not on Dialysis Adverse Reactions Epogen-treated Patients (n = 131) Placebo-treated Patients (n = 79) Hypertension 13.7% 10.1% Arthralgia 12.2% 7.6% Additional serious adverse reactions that occurred in less than 5% of epoetin alfa-treated patients not on dialysis and greater than placebo were erythema (0.8% Epogen and 0% placebo) and myocardial infarction (0.8% Epogen and 0% placebo) [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] . Pediatric Patients In pediatric patients with CKD on dialysis, the pattern of adverse reactions was similar to that found in adults. Zidovudine-treated Patients with HIV- infect ion A total of 297 zidovudine-treated patients with HIV-infection were studied in 4 placebo-controlled studies. A total of 144 (48%) patients were randomly assigned to receive Epogen and 153 (52%) patients were randomly assigned to receive placebo. Epogen was administered at doses between 100 and 200 Units/kg 3 times weekly subcutaneously for up to 12 weeks. For the combined Epogen treatment groups, a total of 141 (98%) men and 3 (2%) women between the ages of 24 and 64 years were enrolled. The racial distribution of the combined Epogen treatment groups was as follows: 129 (90%) white, 8 (6%) black, 1 (1%) Asian, and 6 (4%) other. In double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of 3 months duration involving approximately 300 zidovudine-treated patients with HIV-infection, adverse reactions with an incidence of ≥ 1% in patients treated with Epogen were: Table 5. Adverse Reactions in Zidovudine-treated Patients with HIV-infection Adverse Reaction Epogen (n = 144) Placebo (n = 153) Pyrexia 42% 34% Cough 26% 14% Rash 19% 7% Injection site irritation 7% 4% Urticaria 3% 1% Respiratory tract congestion 1% Not reported Pulmonary embolism 1% Not reported Patients with Cancer on Chemotherapy The data below were obtained in Study C1, a 16-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that enrolled 344 patients with anemia secondary to chemotherapy. There were 333 patients who were evaluable for safety; 168 of 174 patients (97%) randomized to Epogen received at least 1 dose of study drug, and 165 of 170 patients (97%) randomized to placebo received at least 1 placebo dose. For the once weekly Epogen-treatment group, a total of 76 men (45%) and 92 women (55%) between the ages of 20 and 88 years were treated. The racial distribution of the Epogen-treatment group was 158 white (94%) and 10 black (6%). Epogen was administered once weekly for an average of 13 weeks at a dose of 20,000 to 60,000 IU subcutaneously (mean weekly dose was 49,000 IU). The adverse reactions with a reported incidence of ≥ 5% in Epogen-treated patients that occurred at a higher frequency than in placebo-treated patients are shown in the table below: Table 6. Adverse Reactions in Patients with Cancer Adverse Reaction Epogen (n = 168) Placebo (n = 165) Nausea 35% 30% Vomiting 20% 16% Myalgia 10% 5% Arthralgia 10% 6% Stomatitis 10% 8% Cough 9% 7% Weight decrease 9% 5% Leukopenia 8% 7% Bone pain 7% 4% Rash 7% 5% Hyperglycemia 6% 4% Insomnia 6% 2% Headache 5% 4% Depression 5% 4% Dysphagia 5% 2% Hypokalemia 5% 3% Thrombosis 5% 3% Surgery Patients Four hundred sixty-one patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery were studied in a placebo-controlled study (S1) and a comparative dosing study (2 dosing regimens, S2). A total of 358 patients were randomly assigned to receive Epogen and 103 (22%) patients were randomly assigned to receive placebo. Epogen was administered daily at a dose of 100 to 300 IU/kg subcutaneously for 15 days or at 600 IU/kg once weekly for 4 weeks. For the combined Epogen treatment groups, a total of 90 (25%) and 268 (75%) women between the ages of 29 and 89 years were enrolled. The racial distribution of the combined Epogen treatment groups was as follows: 288 (80%) white, 64 (18%) black, 1 (< 1%) Asian, and 5 (1%) other. The adverse reactions with a reported incidence of ≥ 1% in Epogen-treated patients that occurred at a higher frequency than in placebo-treated patients are shown in the table below: Table 7. Adverse Reactions in Surgery Patients Study S1 Study S2 Adverse Reaction Epogen 300 U/kg (n = 112) a Epogen 100 U/kg (n = 101) a Placebo (n = 103) a Epogen 600 U/kg x 4 weeks (n = 73) b Epogen 300 U/kg x 15 days (n = 72) b Nausea 47% 43% 45% 45% 56% Vomiting 21% 12% 14% 19% 28% Pruritus 16% 16% 14% 12% 21% Headache 13% 11% 9% 10% 18% Injection site pain 13% 9% 8% 12% 11% Chills 7% 4% 1% 1% 0% Deep vein thrombosis 6% 3% 3% 0% c 0% c Cough 5% 4% 0% 4% 4% Hypertension 5% 3% 5% 5% 6% Rash 2% 2% 1% 3% 3% Edema 1% 2% 2% 1% 3% a Study included patients undergoing orthopedic surgery treated with Epogen or placebo for 15 days. b Study included patients undergoing orthopedic surgery treated with Epogen 600 U/kg weekly for 4 weeks or 300 U/kg daily for 15 days. c DVTs were determined by clinical symptoms. 6.2 Postmarketing Experience The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Epogen. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4 )] PRCA [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6 )] Serious allergic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7 )] Injection site reactions, including irritation and pain Porphyria Severe Cutaneous Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.8 )] 6.3 Immunogenicity As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to epoetin alfa with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading. Neutralizing antibodies to epoetin alfa that cross-react with endogenous erythropoietin and other ESAs can result in PRCA or severe anemia (with or without other cytopenias) [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6 ) ] .
Contraindications
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS Epogen is contraindicated in patients with: Uncontrolled hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3 )] Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) that begins after treatment with Epogen or other erythropoietin protein drugs [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6 )] Serious allergic reactions to Epogen [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7 )] Epogen from multiple-dose vials contains benzyl alcohol and is contraindicated in: Neonates, infants, pregnant women, and lactating women [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 ), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1 , 8.2 , 8.4 )] . Uncontrolled hypertension ( 4 ) Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) that begins after treatment with Epogen or other erythropoietin protein drugs ( 4 ) Serious allergic reactions to Epogen ( 4 ) Use of the multiple-dose vials containing benzyl alcohol in neonates, infants, pregnant women, and lactating women ( 4 )
Description
11 DESCRIPTION Epoetin alfa is a 165-amino acid erythropoiesis-stimulating glycoprotein manufactured by recombinant DNA technology. It has a molecular weight of approximately 30,400 daltons and is produced by mammalian cells into which the human erythropoietin gene has been introduced. The product contains the identical amino acid sequence of isolated natural erythropoietin. Epogen (epoetin alfa) injection for intravenous or subcutaneous administration is formulated as a sterile, clear, colorless liquid in vials in multiple formulations. Single-dose vials, formulated with an isotonic sodium chloride/sodium citrate-buffered solution, are supplied in multiple strengths. Each single-dose 1 mL vial contains 2,000, 3,000, 4,000, or 10,000 Units of epoetin alfa, Albumin (Human) (2.5 mg), citric acid (0.06 mg), sodium chloride (5.9 mg), and sodium citrate (5.8 mg) in Water for Injection, USP (pH 6.9 ± 0.3). Multiple-dose, 2 mL vials contain 10,000 Units epoetin alfa, albumin (human) (2.5 mg), benzyl alcohol (1%), sodium chloride (8.2 mg), citric acid (0.11 mg), and sodium citrate (1.3 mg) per 1 mL Water for Injection, USP (pH 6.1 ± 0.3). Multiple-dose 1 mL vials contain 20,000 Units epoetin alfa, albumin (human) (2.5 mg), benzyl alcohol (1%), sodium chloride (8.2 mg), citric acid (0.11 mg), and sodium citrate (1.3 mg), per 1 mL in Water for Injection, USP (pH 6.1 ± 0.3).
Dosage And Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Evaluate iron status before and during treatment and maintain iron repletion. Correct or exclude other causes of anemia before initiating treatment ( 2.1 ). In pregnant women, lactating women, neonates, infants: Use only single-dose vials ( 2.1 ). Patients with CKD: Initial dose: 50 to 100 Units/kg 3 times weekly (adults) and 50 Units/kg 3 times weekly (pediatric patients). Individualize maintenance dose. Intravenous route recommended for patients on hemodialysis ( 2.2 ). Patients on Zidovudine due to HIV-infection: 100 Units/kg 3 times weekly ( 2.3 ). Patients with Cancer on Chemotherapy: 40,000 Units weekly or 150 Units/kg 3 times weekly (adults); 600 Units/kg intravenously weekly (pediatric patients ≥ 5 years) ( 2.4 ). Surgery Patients: 300 Units/kg per day daily for 15 days or 600 Units/kg weekly ( 2.5 ). 2.1 Important Dosing Information Evaluation of Iron Stores and Nutritional Factors Evaluate the iron status in all patients before and during treatment. Administer supplemental iron therapy when serum ferritin is less than 100 mcg/L or when serum transferrin saturation is less than 20%. The majority of patients with CKD will require supplemental iron during the course of ESA therapy. Monitoring of Response to Therapy Correct or exclude other causes of anemia (e.g., vitamin deficiency, metabolic or chronic inflammatory conditions, bleeding, etc.) before initiating Epogen. Following initiation of therapy and after each dose adjustment, monitor hemoglobin weekly until the hemoglobin level is stable and sufficient to minimize the need for RBC transfusion. Selection of Formulation In pregnant women, lactating women, neonates, and infants use only single-dose vials (the benzyl alcohol-free formulation) [see Contraindication s ( 4 ) and Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1 , 8.2 , and 8.4 )]. 2.2 Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease In controlled trials, patients experienced greater risks for death, serious adverse cardiovascular reactions, and stroke when administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to target a hemoglobin level of greater than 11 g/dL. No trial has identified a hemoglobin target level, ESA dose, or dosing strategy that does not increase these risks. Individualize dosing and use the lowest dose of Epogen sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )]. Physicians and patients should weigh the possible benefits of decreasing transfusions against the increased risks of death and other serious cardiovascular adverse reactions [see Boxed Warning and Clinical Studies ( 14 ) ] . For all patients with CKD: When initiating or adjusting therapy, monitor hemoglobin levels at least weekly until stable, then monitor at least monthly. When adjusting therapy consider hemoglobin rate of rise, rate of decline, ESA responsiveness and hemoglobin variability. A single hemoglobin excursion may not require a dosing change. Do not increase the dose more frequently than once every 4 weeks. Decreases in dose can occur more frequently. Avoid frequent dose adjustments. If the hemoglobin rises rapidly (e.g., more than 1 g/dL in any 2-week period), reduce the dose of Epogen by 25% or more as needed to reduce rapid responses. For patients who do not respond adequately, if the hemoglobin has not increased by more than 1 g/dL after 4 weeks of therapy, increase the dose by 25%. For patients who do not respond adequately over a 12-week escalation period, increasing the Epogen dose further is unlikely to improve response and may increase risks. Use the lowest dose that will maintain a hemoglobin level sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions. Evaluate other causes of anemia. Discontinue Epogen if responsiveness does not improve. For adult patients with CKD on dialysis: Initiate Epogen treatment when the hemoglobin level is less than 10 g/dL. If the hemoglobin level approaches or exceeds 11 g/dL, reduce or interrupt the dose of Epogen. The recommended starting dose for adult patients is 50 to 100 Units/kg 3 times weekly intravenously or subcutaneously. The intravenous route is recommended for patients on hemodialysis. For adult patients with CKD not on dialysis: Consider initiating Epogen treatment only when the hemoglobin level is less than 10 g/dL and the following considerations apply: ○ The rate of hemoglobin decline indicates the likelihood of requiring a RBC transfusion and , ○ Reducing the risk of alloimmunization and/or other RBC transfusion-related risks is a goal If the hemoglobin level exceeds 10 g/dL, reduce or interrupt the dose of Epogen, and use the lowest dose of Epogen sufficient to reduce the need for RBC transfusions. The recommended starting dose for adult patients is 50 to 100 Units/kg 3 times weekly intravenously or subcutaneously. For pediatric patients with CKD: • Initiate Epogen treatment only when the hemoglobin level is less than 10 g/dL. • If the hemoglobin level approaches or exceeds 12 g/dL, reduce or interrupt the dose of Epogen. • The recommended starting dose for pediatric patients (ages 1 month or older) is 50 Units/kg 3 times weekly intravenously or subcutaneously. When treating patients who have chronic kidney disease and cancer, physicians should refer to Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 and 5.2 ). 2.3 Zidovudine-treated Patients with HIV-infection Starting Dose The recommended starting dose in adults is 100 Units/kg as an intravenous or subcutaneous injection 3 times per week. Dose Adjustment If hemoglobin does not increase after 8 weeks of therapy, increase Epogen dose by approximately 50 to 100 Units/kg at 4- to 8-week intervals until hemoglobin reaches a level needed to avoid RBC transfusions or 300 Units/kg. Withhold Epogen if hemoglobin exceeds 12 g/dL. Resume therapy at a dose 25% below the previous dose when hemoglobin declines to less than 11 g/dL. Discontinue Epogen if an increase in hemoglobin is not achieved at a dose of 300 Units/kg for 8 weeks. 2.4 Patients on Cancer Chemotherapy Initiate Epogen in patients on cancer chemotherapy only if the hemoglobin is less than 10 g/dL, and if there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy. Use the lowest dose of Epogen necessary to avoid RBC transfusions. Recommended Starting Dose Adults: 150 Units/kg subcutaneously 3 times per week until completion of a chemotherapy course or 40,000 Units subcutaneously weekly until completion of a chemotherapy course. Pediatric Patients (5 to 18 years): 600 Units/kg intravenously weekly until completion of a chemotherapy course. Dose Reduction Reduce dose by 25% if: Hemoglobin increases greater than 1 g/dL in any 2-week period or Hemoglobin reaches a level needed to avoid RBC transfusion. Withhold dose if hemoglobin exceeds a level needed to avoid RBC transfusion. Reinitiate at a dose 25% below the previous dose when hemoglobin approaches a level where RBC transfusions may be required. Dose Increase After the initial 4 weeks of Epogen therapy, if hemoglobin increases by less than 1 g/dL and remains below 10 g/dL, increase dose to: 300 Units/kg three times per week in adults or 60,000 Units weekly in adults 900 Units/kg (maximum 60,000 Units) weekly in pediatric patients After 8 weeks of therapy, if there is no response as measured by hemoglobin levels or if RBC transfusions are still required, discontinue Epogen. 2.5 Surgery Patients The recommended Epogen regimens are: 300 Units/kg per day subcutaneously for 15 days total: administered daily for 10 days before surgery, on the day of surgery, and for 4 days after surgery. 600 Units/kg subcutaneously in 4 doses administered 21, 14, and 7 days before surgery and on the day of surgery. Deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis is recommended during Epogen therapy [see Warning s and Precautions ( 5.1 ) ] . 2.6 Preparation and Administration Do not shake. Do not use Epogen that has been shaken or frozen. Protect vials from light. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use any vials exhibiting particulate matter or discoloration. Discard unused portions of Epogen in preservative-free vials. Do not re-enter preservative-free vials. Store unused portions of Epogen in multiple-dose vials at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Discard 21 days after initial entry. Do not dilute. Do not mix with other drug solutions except for admixing as described below: Preservative-free Epogen from single-dose vials may be admixed in a syringe with bacteriostatic 0.9% sodium chloride injection, USP, with benzyl alcohol 0.9% (bacteriostatic saline) in a 1:1 ratio using aseptic technique at the time of administration. Do not mix Epogen with bacteriostatic saline when administering to pregnant women, lactating women, neonates, and infants [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1 , 8.2 , 8.4 )].
Indications And Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Epogen is an erythropoiesis-stimulating agent (ESA) indicated for: Treatment of anemia due to - Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in patients on dialysis and not on dialysis ( 1.1 ). - Zidovudine in patients with HIV-infection ( 1.2 ). - The effects of concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy, and upon initiation, there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy ( 1.3 ). Reduction of allogeneic RBC transfusions in patients undergoing elective, noncardiac, nonvascular surgery ( 1.4 ). Limitations of Use Epogen has not been shown to improve quality of life, fatigue, or patient well-being ( 1.5 ). Epogen is not indicated for use: In patients with cancer receiving hormonal agents, biologic products, or radiotherapy, unless also receiving concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy ( 1.5 ). In patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy when the anticipated outcome is cure ( 1.5 ). In patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy in whom the anemia can be managed by transfusion ( 1.5 ). In patients scheduled for surgery who are willing to donate autologous blood ( 1.5 ). In patients undergoing cardiac or vascular surgery ( 1.5 ). As a substitute for RBC transfusions in patients who require immediate correction of anemia ( 1.5 ). 1.1 Anemia Due to Chronic Kidney Disease Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia due to chronic kidney disease (CKD), including patients on dialysis and not on dialysis to decrease the need for red blood cell (RBC) transfusion. 1.2 Anemia Due to Zidovudine in Patients with HIV-infection Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia due to zidovudine administered at ≤ 4200 mg/week in patients with HIV-infection with endogenous serum erythropoietin levels of ≤ 500 mUnits/mL. 1.3 Anemia Due to Chemotherapy in Patients With Cancer Epogen is indicated for the treatment of anemia in patients with non-myeloid malignancies where anemia is due to the effect of concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy, and upon initiation, there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy. 1.4 Reduction of Allogeneic Red Blood Cell Transfusions in Patients Undergoing Elective, Noncardiac, Nonvascular Surgery Epogen is indicated to reduce the need for allogeneic RBC transfusions among patients with perioperative hemoglobin > 10 to ≤ 13 g/dL who are at high risk for perioperative blood loss from elective, noncardiac, nonvascular surgery. Epogen is not indicated for patients who are willing to donate autologous blood pre-operatively. 1.5 Limitations of Use Epogen has not been shown to improve quality of life, fatigue, or patient well-being. Epogen is not indicated for use: In patients with cancer receiving hormonal agents, biologic products, or radiotherapy, unless also receiving concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy. In patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy when the anticipated outcome is cure. In patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy in whom the anemia can be managed by transfusion. In patients scheduled for surgery who are willing to donate autologous blood. In patients undergoing cardiac or vascular surgery. As a substitute for RBC transfusions in patients who require immediate correction of anemia.
Overdosage
10 OVERDOSAGE Epogen overdosage can cause hemoglobin levels above the desired level, which should be managed with discontinuation or reduction of Epogen dosage and/or with phlebotomy, as clinically indicated [see Pharmacodynamics ( 12.2 )]. Cases of severe hypertension have been observed following overdose with ESAs [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3 )] .
Adverse Reactions Table
| Adverse Reaction | Epogen-treated Patients (n = 148) | Placebo-treated Patients (n = 96) |
| Hypertension | 27.7% | 12.5% |
| Arthralgia | 16.2% | 3.1% |
| Muscle spasm | 7.4% | 6.3% |
| Pyrexia | 10.1% | 8.3% |
| Dizziness | 9.5% | 8.3% |
| Medical Device Malfunction (artificial kidney clotting during dialysis) | 8.1% | 4.2% |
| Vascular Occlusion (vascular access thrombosis) | 8.1% | 2.1% |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 6.8% | 5.2% |
Clinical Pharmacology
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 12.1 Mechanism of Action Epogen stimulates erythropoiesis by the same mechanism as endogenous erythropoietin. 12.2 Pharmacodynamics Epogen increases the reticulocyte count within 10 days of initiation, followed by increases in the RBC count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, usually within 2 to 6 weeks. The rate of hemoglobin increase varies among patients and is dependent upon the dose of Epogen administered. For correction of anemia in hemodialysis patients, a greater biologic response is not observed at doses exceeding 300 Units/kg 3 times weekly. 12.3 Pharmacokinetics In adult and pediatric patients with CKD, the elimination half-life (t 1/2 ) of plasma erythropoietin after intravenous administration of Epogen ranged from 4 to 13 hours. After subcutaneous administration, C max was achieved within 5 to 24 hours. The t 1/2 in adult patients with serum creatinine greater than 3 mg/dL was similar between those not on dialysis and those maintained on dialysis. The pharmacokinetic data indicate no apparent difference in Epogen t 1/2 among adult patients above or below 65 years of age. A pharmacokinetic study comparing 150 Units/kg subcutaneous 3 times weekly to 40,000 Units subcutaneous weekly dosing regimen was conducted for 4 weeks in healthy subjects (n = 12) and for 6 weeks in anemic cancer patients (n = 32) receiving cyclic chemotherapy. There was no accumulation of serum erythropoietin after the 2 dosing regimens during the study period. The 40,000 Units weekly regimen had a higher C max (3- to 7-fold), longer T max (2- to 3-fold), higher AUC 0-168 h (2- to 3-fold) of erythropoietin and lower clearance (CL) (50%) than the 150 Units/kg 3 times weekly regimen. In anemic cancer patients, the average t 1/2 was similar (40 hours with range of 16 to 67 hours) after both dosing regimens. After the 150 Units/kg 3 times weekly dosing, the values of T max and CL were similar (13.3 ± 12.4 vs. 14.2 ± 6.7 hours, and 20.2 ± 15.9 vs. 23.6 ± 9.5 mL/hr/kg) between week 1 when patients were receiving chemotherapy (n = 14) and week 3 when patients were not receiving chemotherapy (n = 4). Differences were observed after the 40,000 Units weekly dosing with longer T max (38 ± 18 hours) and lower CL (9.2 ± 4.7 mL/hr/kg) during week 1 when patients were receiving chemotherapy (n = 18) compared with those (22 ± 4.5 hours, 13.9 ± 7.6 mL/hr/kg, respectively) during week 3 when patients were not receiving chemotherapy (n = 7). The pharmacokinetic profile of Epogen in pediatric patients appeared similar to that of adults. The pharmacokinetics of Epogen has not been studied in patients with HIV-infection.
Mechanism Of Action
12.1 Mechanism of Action Epogen stimulates erythropoiesis by the same mechanism as endogenous erythropoietin.
Pharmacodynamics
12.2 Pharmacodynamics Epogen increases the reticulocyte count within 10 days of initiation, followed by increases in the RBC count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, usually within 2 to 6 weeks. The rate of hemoglobin increase varies among patients and is dependent upon the dose of Epogen administered. For correction of anemia in hemodialysis patients, a greater biologic response is not observed at doses exceeding 300 Units/kg 3 times weekly.
Pharmacokinetics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics In adult and pediatric patients with CKD, the elimination half-life (t 1/2 ) of plasma erythropoietin after intravenous administration of Epogen ranged from 4 to 13 hours. After subcutaneous administration, C max was achieved within 5 to 24 hours. The t 1/2 in adult patients with serum creatinine greater than 3 mg/dL was similar between those not on dialysis and those maintained on dialysis. The pharmacokinetic data indicate no apparent difference in Epogen t 1/2 among adult patients above or below 65 years of age. A pharmacokinetic study comparing 150 Units/kg subcutaneous 3 times weekly to 40,000 Units subcutaneous weekly dosing regimen was conducted for 4 weeks in healthy subjects (n = 12) and for 6 weeks in anemic cancer patients (n = 32) receiving cyclic chemotherapy. There was no accumulation of serum erythropoietin after the 2 dosing regimens during the study period. The 40,000 Units weekly regimen had a higher C max (3- to 7-fold), longer T max (2- to 3-fold), higher AUC 0-168 h (2- to 3-fold) of erythropoietin and lower clearance (CL) (50%) than the 150 Units/kg 3 times weekly regimen. In anemic cancer patients, the average t 1/2 was similar (40 hours with range of 16 to 67 hours) after both dosing regimens. After the 150 Units/kg 3 times weekly dosing, the values of T max and CL were similar (13.3 ± 12.4 vs. 14.2 ± 6.7 hours, and 20.2 ± 15.9 vs. 23.6 ± 9.5 mL/hr/kg) between week 1 when patients were receiving chemotherapy (n = 14) and week 3 when patients were not receiving chemotherapy (n = 4). Differences were observed after the 40,000 Units weekly dosing with longer T max (38 ± 18 hours) and lower CL (9.2 ± 4.7 mL/hr/kg) during week 1 when patients were receiving chemotherapy (n = 18) compared with those (22 ± 4.5 hours, 13.9 ± 7.6 mL/hr/kg, respectively) during week 3 when patients were not receiving chemotherapy (n = 7). The pharmacokinetic profile of Epogen in pediatric patients appeared similar to that of adults. The pharmacokinetics of Epogen has not been studied in patients with HIV-infection.
Effective Time
20180725
Version
133
Dosage Forms And Strengths
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Injection: ○ 2,000 Units/mL, 3,000 Units/mL, 4,000 Units/mL, and 10,000 Units/mL of Epogen as a clear and colorless liquid in single-dose vials ○ 20,000 Units/2 mL (10,000 Units/mL) and 20,000 Units/mL of Epogen as a clear and colorless liquid in multiple-dose vials (contains benzyl alcohol). Injection ○ 2,000 Units/mL, 3,000 Units/mL, 4,000 Units/mL, and 10,000 Units/mL in single-dose vials ( 3 ) ○ 20,000 Units/2 mL (10,000 Units/mL) and 20,000 Units/mL in multiple-dose vials containing benzyl alcohol ( 3 )
Spl Product Data Elements
EPOGEN epoetin alfa EPOETIN ERYTHROPOIETIN SODIUM CHLORIDE SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE ALBUMIN HUMAN EPOGEN epoetin alfa EPOETIN ERYTHROPOIETIN SODIUM CHLORIDE SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM ALBUMIN HUMAN CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE EPOGEN epoetin alfa EPOETIN ERYTHROPOIETIN SODIUM CHLORIDE SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM ALBUMIN HUMAN CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE EPOGEN epoetin alfa EPOETIN ERYTHROPOIETIN SODIUM CHLORIDE SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM ALBUMIN HUMAN CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE EPOGEN epoetin alfa EPOETIN ERYTHROPOIETIN SODIUM CHLORIDE ALBUMIN HUMAN SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE BENZYL ALCOHOL EPOGEN epoetin alfa EPOETIN ERYTHROPOIETIN SODIUM CHLORIDE ALBUMIN HUMAN SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE BENZYL ALCOHOL
Carcinogenesis And Mutagenesis And Impairment Of Fertility
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility The carcinogenic potential of Epogen has not been evaluated. Epogen was not mutagenic or clastogenic under the conditions tested: Epogen was negative in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test), in the in vitro mammalian cell gene mutation assay (the hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase [HGPRT] locus), in an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in mammalian cells, and in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. When administered intravenously to male and female rats prior to and during mating, and to females through the beginning of implantation (up to gestational day 7; dosing stopped prior to the beginning of organogenesis), doses of 100 and 500 Units/kg/day of Epogen caused slight increases in pre-implantation loss, post-implantation loss and decreases in the incidence of live fetuses. It is not clear whether these effects reflect a drug effect on the uterine environment or on the conceptus. This animal dose level of 100 Units/kg/day approximates the clinical recommended starting dose, depending on the patient’s treatment indication, but may be lower than the clinical dose in patients whose doses have been adjusted.
Nonclinical Toxicology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility The carcinogenic potential of Epogen has not been evaluated. Epogen was not mutagenic or clastogenic under the conditions tested: Epogen was negative in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test), in the in vitro mammalian cell gene mutation assay (the hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase [HGPRT] locus), in an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in mammalian cells, and in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. When administered intravenously to male and female rats prior to and during mating, and to females through the beginning of implantation (up to gestational day 7; dosing stopped prior to the beginning of organogenesis), doses of 100 and 500 Units/kg/day of Epogen caused slight increases in pre-implantation loss, post-implantation loss and decreases in the incidence of live fetuses. It is not clear whether these effects reflect a drug effect on the uterine environment or on the conceptus. This animal dose level of 100 Units/kg/day approximates the clinical recommended starting dose, depending on the patient’s treatment indication, but may be lower than the clinical dose in patients whose doses have been adjusted.
Application Number
BLA103234
Brand Name
EPOGEN
Generic Name
epoetin alfa
Product Ndc
55513-144
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
INTRAVENOUS,SUBCUTANEOUS
Package Label Principal Display Panel
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL NDC 55513-126-10 10 x 2000 Units/mL Single Dose Vials AMGEN ® EPOGEN ® EPOETIN ALFA recombinant 2000 Units/mL 2000 Units/mL Single Dose Vials (containing 1 mL) For Intravenous or Subcutaneous Use Only Sterile Solution – No Preservative Store at 2˚ to 8˚C (36˚ to 46˚F). Do Not Freeze or Shake. Manufactured by Amgen Inc. Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799 U.S.A. U.S. License No. 1080 ©2012,2017 Amgen Inc. Rx Only PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL NDC 55513-126-10 10 x 2000 Units/mL Single Dose Vials AMGEN® EPOGEN® EPOETIN ALFA recombinant 2000 Units/mL 2000 Units/mL Single Dose Vials (containing 1 mL) For Intravenous or Subcutaneous Use Only Sterile Solution – No Preservative Store at 2˚ to 8˚C (36˚ to 46˚F). Do Not Freeze or Shake. Manufactured by Amgen Inc. Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799 U.S.A. U.S. License No. 1080 ©2012,2017 Amgen Inc. Rx Only
Recent Major Changes
• Dosage and Administration, Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease ( 2.2 ) 9/2017 • Warnings and Precautions, Increased Mortality and/or Increased Risk of Tumor Progression or Recurrence in Patients With Cancer ( 5.2 ) 7/2018 • Warnings and Precautions, Severe Cutaneous Reactions ( 5.8 ) 9/2017 • Warnings and Precautions, Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions Due to Benzyl Alcohol Preservative ( 5.9 ) 9/2017
Recent Major Changes Table
| • Dosage and Administration, Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease ( | 9/2017 |
| • Warnings and Precautions, Increased Mortality and/or Increased Risk of Tumor Progression or Recurrence in Patients With Cancer ( | 7/2018 |
| • Warnings and Precautions, Severe Cutaneous Reactions ( | 9/2017 |
| • Warnings and Precautions, Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions Due to Benzyl Alcohol Preservative ( | 9/2017 |
Information For Patients
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling ( Medication Guide and Instructions for Use ). Inform patients: Of the increased risks of mortality, serious cardiovascular reactions, thromboembolic reactions, stroke, and tumor progression [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 , 5.2 )] . To undergo regular blood pressure monitoring, adhere to prescribed anti-hypertensive regimen and follow recommended dietary restrictions. To contact their healthcare provider for new-onset neurologic symptoms or change in seizure frequency. Of the need to have regular laboratory tests for hemoglobin. Risks are associated with benzyl alcohol in neonates, infants, pregnant women, and lactating women [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1 , 8.2 , 8.4 )]. Instruct patients who self-administer Epogen of the: Importance of following the Instructions for Use. Dangers of reusing needles, syringes, or unused portions of single-dose vials. Proper disposal of used syringes, needles, and unused vials, and of the full container. Epogen ® (epoetin alfa) Manufactured by: Amgen Inc. One Amgen Center Drive Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799 U.S.A. U.S. License Number 1080 ©1989-2018 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved. 1xxxxxx- v33
Spl Medguide
MEDICATION GUIDE Epogen ® (Ee-po-jen) (epoetin alfa) Read this Medication Guide: before you start Epogen. if you are told by your healthcare provider that there is new information about Epogen. if you are told by your healthcare provider that you may inject Epogen at home, read this Medication Guide each time you receive a new supply of medicine. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. Talk with your healthcare provider regularly about the use of Epogen and ask if there is new information about Epogen. What is the most important information I should know about Epogen? Epogen may cause serious side effects that can lead to death, including: For people with cancer: Your tumor may grow faster and you may die sooner if you choose to take Epogen. Your healthcare provider will talk with you about these risks. For all people who take Epogen, including people with cancer or chronic kidney disease: Serious heart problems, such as heart attack or heart failure, and stroke. You may die sooner if you are treated with Epogen to increase red blood cells (RBCs) to near the same level found in healthy people. Blood clots. Blood clots may happen at any time while taking Epogen. If you are receiving Epogen for any reason and you are going to have surgery, talk to your healthcare provider about whether or not you need to take a blood thinner to lessen the chance of blood clots during or following surgery. Blood clots can form in blood vessels (veins), especially in your leg (deep venous thrombosis or DVT). Pieces of a blood clot may travel to the lungs and block the blood circulation in the lungs (pulmonary embolus). Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms: ○ Chest pain ○ Trouble breathing or shortness of breath ○ Pain in your legs, with or without swelling ○ A cool or pale arm or leg ○ Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or trouble understanding others’ speech ○ Sudden numbness or weakness in your face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of your body ○ Sudden trouble seeing ○ Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination ○ Loss of consciousness (fainting) ○ Hemodialysis vascular access stops working See “What are the possible side effects of Epogen?” below for more information. If you decide to take Epogen, your healthcare provider should prescribe the smallest dose of Epogen that is necessary to reduce your chance of needing RBC transfusions. What is Epogen? Epogen is a prescription medicine used to treat anemia. People with anemia have a lower-than-normal number of RBCs. Epogen works like the human protein called erythropoietin to help your body make more RBCs. Epogen is used to reduce or avoid the need for RBC transfusions. Epogen may be used to treat anemia if it is caused by: Chronic kidney disease (you may or may not be on dialysis). Chemotherapy that will be used for at least two months after starting Epogen. A medicine called zidovudine (AZT) used to treat HIV infection. Epogen may also be used to reduce the chance you will need RBC transfusions if you are scheduled for certain surgeries where a lot of blood loss is expected. If your hemoglobin level stays too high or if your hemoglobin goes up too quickly, this may lead to serious health problems which may result in death. These serious health problems may happen if you take Epogen, even if you do not have an increase in your hemoglobin level. Epogen has not been proven to improve quality of life, fatigue, or well-being. Epogen should not be used for treatment of anemia: If you have cancer and you will not be receiving chemotherapy that may cause anemia. If you have a cancer that has a high chance of being cured. Talk with your healthcare provider about the kind of cancer you have. If your anemia caused by chemotherapy treatment can be managed by RBC transfusion. In place of emergency treatment for anemia (RBC transfusions). Epogen should not be used to reduce the chance you will need RBC transfusions if: You are scheduled for surgery on your heart or blood vessels. You are able and willing to donate blood prior to surgery. It is not known if Epogen is safe and effective in treating anemia in children less than 1 month old who have chronic kidney disease and in children less than 5 years old who have anemia caused by chemotherapy. Who should not take Epogen? Do not take Epogen if you : Have cancer and have not been counseled by your healthcare provider about treatment with Epogen. Have high blood pressure that is not controlled (uncontrolled hypertension). Have been told by your healthcare provider that you have or have ever had a type of anemia called Pure Red Cell Aplasia (PRCA) that starts after treatment with Epogen or other erythropoietin protein medicines. Have had a serious allergic reaction to Epogen. Do not give Epogen from multiple-dose vials to: Pregnant or breastfeeding women Babies Before taking EPOGEN, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: Have heart disease. Have high blood pressure. Have had a seizure (convulsion) or stroke. Receive dialysis treatment. Are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Epogen may harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about possible pregnancy and birth control choices that are right for you. Are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Epogen passes into breast milk. Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. How should I take Epogen? If you or your caregiver has been trained to give Epogen shots (injections) at home: ○ Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the “Instructions for Use” that come with Epogen. ○ Take Epogen exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to. Do not change the dose of Epogen unless told to do so by your healthcare provider. ○ Your healthcare provider will show you how much Epogen to use, how to inject it, how often it should be injected, and how to safely throw away the used vials, syringes, and needles. ○ If you miss a dose of Epogen, call your healthcare provider right away and ask what to do. ○ If you take more than the prescribed dose of Epogen, call your healthcare provider right away. During treatment with Epogen, continue to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for diet and medicines. Have your blood pressure checked as instructed by your healthcare provider. What are the possible side effects of Epogen? Epogen may cause serious side effects, including: See “ What is the most important information I should know about Epogen? ” High blood pressure . High blood pressure is a common side effect of Epogen in people with chronic kidney disease. Your blood pressure may go up or be difficult to control with blood pressure medicine while taking Epogen. This can happen even if you have never had high blood pressure before. Your healthcare provider should check your blood pressure often. If your blood pressure does go up, your healthcare provider may prescribe new or more blood pressure medicine. Seizures . If you have any seizures while taking Epogen, get medical help right away and tell your healthcare provider. Antibodies to Epogen . Your body may make antibodies to Epogen. These antibodies can block or lessen your body’s ability to make RBCs and cause you to have severe anemia. Call your healthcare provider if you have unusual tiredness, lack of energy, dizziness, or fainting. You may need to stop taking Epogen. Serious allergic reactions . Serious allergic reactions can cause a skin rash, itching, shortness of breath, wheezing, dizziness and fainting because of a drop in blood pressure, swelling around your mouth or eyes, fast pulse, or sweating. If you have a serious allergic reaction, stop using Epogen and call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away. Severe skin reactions . Signs and symptoms of severe skin reactions with Epogen may include: skin rash with itching, blisters, skin sores, peeling, or areas of skin coming off. If you have any signs or symptoms of a severe skin reaction, stop using Epogen and call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away. Dangers of using Epogen from multiple-dose vials in newborns, infants, and pregnant or breastfeeding women. Do not use Epogen from multiple-dose vials in newborns, infants, pregnant or breastfeeding women because the Epogen in these vials contains benzyl alcohol. Benzyl alcohol has been shown to cause brain damage, other serious side effects, and death in newborn and premature babies. If you use Epogen from multiple-dose vials you should not breastfeed for at least 2 weeks after the last dose. Epogen that comes in single-dose vials does not contain benzyl alcohol. See “ Who should not take Epogen? ” Common side effects of Epogen include: • joint, muscle, or bone pain • rash • soreness of mouth • fever • nausea • itching • cough • vomiting • headache • dizziness • blood vessel blockage • respiratory infection • high blood sugar • low white blood cells • weight decrease • low potassium levels in the blood • trouble sleeping • depression • chills • difficulty swallowing • muscle spasm • redness and pain at the Epogen injection site These are not all of the possible side effects of Epogen. Your healthcare provider can give you a more complete list. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effects that bother you or that do not go away. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. How should I store Epogen? Do not shake Epogen. Store Epogen vials in the carton it comes in to protect from light. Store Epogen in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Do not freeze Epogen . Do not use Epogen that has been frozen. Throw away multiple-dose vials of Epogen no later than 21 days from the first day that you put a needle into the vial. Single-dose vials of Epogen should be used only one time. Throw the vial away after use even if there is medicine left in the vial. Keep Epogen and all medicines out of the reach of children. General information about Epogen Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Epogen for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Epogen to other people even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Epogen that is written for healthcare professionals. What are the ingredients in Epogen? Active ingredient: epoetin alfa Inactive ingredients: Multiple-dose vials contain benzyl alcohol. All vials contain albumin (human), citric acid, sodium chloride, sodium citrate, and Water for Injection. Manufactured by: Amgen Inc. One Amgen Center Drive Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799 U.S.A. ©1989-2017 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved. 1xxxxxx- v8 For more information, go to the following website: www.epogen.com or call 1-800-77-AMGEN This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: 9/2017
Spl Medguide Table
| MEDICATION GUIDE Epogen® (Ee-po-jen) (epoetin alfa) | ||
| Read this Medication Guide: | ||
| What is the most important information I should know about Epogen? Epogen may cause serious side effects that can lead to death, including: For people with cancer: | ||
| What is Epogen? Epogen is a prescription medicine used to treat anemia. People with anemia have a lower-than-normal number of RBCs. Epogen works like the human protein called erythropoietin to help your body make more RBCs. Epogen is used to reduce or avoid the need for RBC transfusions. Epogen may be used to treat anemia if it is caused by: | ||
| Who should not take Epogen? Do not take Epogen if you: | ||
| Before taking EPOGEN, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | ||
| How should I take Epogen? | ||
| What are the possible side effects of Epogen? Epogen may cause serious side effects, including: | ||
| • joint, muscle, or bone pain | • rash | • soreness of mouth |
| • fever | • nausea | • itching |
| • cough | • vomiting | • headache |
| • dizziness | • blood vessel blockage | • respiratory infection |
| • high blood sugar | • low white blood cells | • weight decrease |
| • low potassium levels in the blood | • trouble sleeping | • depression |
| • chills | • difficulty swallowing | • muscle spasm |
| • redness and pain at the Epogen injection site These are not all of the possible side effects of Epogen. Your healthcare provider can give you a more complete list. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effects that bother you or that do not go away. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||
| How should I store Epogen? | ||
| General information about Epogen Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Epogen for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Epogen to other people even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Epogen that is written for healthcare professionals. | ||
| What are the ingredients in Epogen? Active ingredient: epoetin alfa Inactive ingredients: | ||
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: 9/2017 | ||
Spl Patient Package Insert Table
| Instructions for Use Epogen® (Ee-po-jen) (epoetin alfa) |
Clinical Studies
14 CLINICAL STUDIES 14.1 Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Adult Patients on Dialysi s Patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis: ESA effects on rates of transfusion In clinical studies of patients with CKD on dialysis, Epogen increased hemoglobin levels and decreased the need for RBC transfusion. Overall, more than 95% of patients were RBC transfusion-independent after receiving Epogen for 3 months. In clinical studies at starting doses of 50 to 150 Units/kg 3 times weekly, adult patients responded with an average rate of hemoglobin rise as presented in Table 8. Table 8: Average Rate of Hemoglobin Rise in 2 Weeks Starting Dose (3 Times Weekly Intravenously) Hemoglobin Inc rease in 2 Weeks 50 Units/kg 0.5 g/dL 100 Units/kg 0.8 g/dL 150 Units/kg 1.2 g/dL The safety and efficacy of Epogen were evaluated in 13 clinical studies involving intravenous administration to a total of 1010 patients on dialysis with anemia. Overall, more than 90% of the patients treated with Epogen experienced improvement in hemoglobin concentrations. In the 3 largest of these clinical studies, the median maintenance dose necessary to maintain the hemoglobin between 10 to 12 g/dL was approximately 75 Units/kg 3 times weekly. More than 95% of patients were able to avoid RBC transfusions. In the largest US multicenter study, approximately 65% of the patients received doses of 100 Units/kg 3 times weekly or less to maintain their hemoglobin at approximately 11.7 g/dL. Almost 10% of patients received a dose of 25 Units/kg or less, and approximately 10% received a dose of more than 200 Units/kg 3 times weekly to maintain their hemoglobin at this level. In the Normal Hematocrit Study, the yearly transfusion rate was 51.5% in the lower hemoglobin group (10 g/dL) and 32.4% in the higher hemoglobin group (14 g/dL). Other ESA trials In a 26-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 118 patients on dialysis with an average hemoglobin of approximately 7 g/dL were randomized to either Epogen or placebo. By the end of the study, average hemoglobin increased to approximately 11 g/dL in the Epogen-treated patients and remained unchanged in patients receiving placebo. Epogen-treated patients experienced improvements in exercise tolerance and patient-reported physical functioning at month 2 that were maintained throughout the study. A multicenter, unit-dose study was also conducted in 119 patients receiving peritoneal dialysis who self-administered Epogen subcutaneously. Patients responded to Epogen administered subcutaneously in a manner similar to patients receiving intravenous administration. Pediatric Patients with CKD on Dialysis The safety and efficacy of Epogen were studied in a placebo-controlled, randomized study of 113 pediatric patients with anemia (hemoglobin ≤ 9 g/dL) undergoing peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis. The initial dose of Epogen was 50 Units/kg intravenously or subcutaneously 3 times weekly. The dose of study drug was titrated to achieve either a hemoglobin of 10 to 12 g/dL or an absolute increase in hemoglobin of 2 g/dL over baseline. At the end of the initial 12 weeks, a statistically significant rise in mean hemoglobin (3.1 g/dL vs. 0.3 g/dL) was observed only in the Epogen arm. The proportion of pediatric patients achieving a hemoglobin of 10 g/dL, or an increase in hemoglobin of 2 g/dL over baseline, at any time during the first 12 weeks was higher in the Epogen arm (96% vs. 58%). Within 12 weeks of initiating Epogen therapy, 92.3% of the pediatric patients were RBC transfusion independent as compared to 65.4% who received placebo. Among patients who received 36 weeks of Epogen, hemodialysis patients received a higher median maintenance dose [167 Units/kg/week (n = 28) vs. 76 Units/kg/week (n = 36)] and took longer to achieve a hemoglobin of 10 to 12 g/dL (median time to response 69 days vs. 32 days) than patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. Adult Patients With CKD Not Requiring Dialysis Four clinical studies were conducted in patients with CKD not on dialysis involving 181 patients treated with Epogen. These patients responded to Epogen therapy in a manner similar to that observed in patients on dialysis. Patients with CKD not on dialysis demonstrated a dose-dependent and sustained increase in hemoglobin when Epogen was administered by either an intravenous or subcutaneous route, with similar rates of rise of hemoglobin when Epogen was administered by either route. Patients with c hronic kidney disease not on dialysis : ESA effects on rates of transfusion In TREAT, a randomized, double-blind trial of 4038 patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes not on dialysis, a post-hoc analysis showed that the proportion of patients receiving RBC transfusions was lower in patients administered an ESA to target a hemoglobin of 13 g/dL compared to the control arm in which an ESA was administered intermittently if hemoglobin concentration decreased to less than 9 g/dL (15% versus 25%, respectively). In CHOIR, a randomized open-label study of 1432 patients with CKD not on dialysis, use of epoetin alfa to target a higher (13.5 g/dL) versus lower (11.3 g/dL) hemoglobin goal did not reduce the use of RBC transfusions. In each trial, no benefits occurred for the cardiovascular or end-stage renal disease outcomes. In each trial, the potential benefit of ESA therapy was offset by worse cardiovascular safety outcomes resulting in an unfavorable benefit-risk profile [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] . ESA Effects on rates of death and other serious cardiac adverse reaction s Three randomized outcome trials (Normal Hematocrit Study [NHS], Correction of Anemia with Epoetin Alfa in Chronic Kidney Disease [CHOIR], and Trial of Darbepoetin Alfa in Type 2 Diabetes and CKD [TREAT]) have been conducted in patients with CKD using Epogen/PROCRIT/Aranesp to target higher vs. lower hemoglobin levels. Though these trials were designed to establish a cardiovascular or renal benefit of targeting higher hemoglobin levels, in all 3 studies, patients randomized to the higher hemoglobin target experienced worse cardiovascular outcomes and showed no reduction in progression to ESRD. In each trial, the potential benefit of ESA therapy was offset by worse cardiovascular safety outcomes resulting in an unfavorable benefit-risk profile [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] . 14.2 Zidovudine-treated Patients With HIV-infection The safety and efficacy of Epogen were evaluated in 4 placebo-controlled studies enrolling 297 anemic patients (hemoglobin < 10 g/dL) with HIV-infection receiving concomitant therapy with zidovudine. In the subgroup of patients (89/125 Epogen and 88/130 placebo) with pre-study endogenous serum erythropoietin levels ≤ 500 mUnits/mL, Epogen reduced the mean cumulative number of units of blood transfused per patient by approximately 40% as compared to the placebo group. Among those patients who required RBC transfusions at baseline, 43% of patients treated with Epogen versus 18% of placebo-treated patients were RBC transfusion-independent during the second and third months of therapy. Epogen therapy also resulted in significant increases in hemoglobin in comparison to placebo. When examining the results according to the weekly dose of zidovudine received during month 3 of therapy, there was a statistically significant reduction (p < 0.003) in RBC transfusion requirements in patients treated with Epogen (n = 51) compared to placebo-treated patients (n = 54) whose mean weekly zidovudine dose was ≤ 4200 mg/week. Approximately 17% of the patients with endogenous serum erythropoietin levels ≤ 500 mUnits/mL receiving Epogen in doses from 100 to 200 Units/kg 3 times weekly achieved a hemoglobin of 12.7 g/dL without administration of RBC transfusions or significant reduction in zidovudine dose. In the subgroup of patients whose pre-study endogenous serum erythropoietin levels were > 500 mUnits/mL, Epogen therapy did not reduce RBC transfusion requirements or increase hemoglobin compared to the corresponding responses in placebo-treated patients. 14.3 Patients with Cancer on Chemotherapy The safety and effectiveness of Epogen was assessed in two multicenter, randomized (1:1), placebo-controlled, double-blind studies (Study C1 and Study C2) and a pooled analysis of six additional randomized (1:1), multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies. All studies were conducted in patients with anemia due to concomitantly administered cancer chemotherapy. Study C1 enrolled 344 adult patients, Study C2 enrolled 222 pediatric patients, and the pooled analysis contained 131 patients randomized to epoetin alfa or placebo. In Studies C1 and C2, efficacy was demonstrated by a reduction in the proportion of patients who received an RBC transfusion, from week 5 through end of the study, with the last-known RBC transfusion status carried forward for patients who discontinued treatment. In the pooled analysis, efficacy was demonstrated by a reduction in the proportion of patients who received an RBC transfusion from week 5 through end of the study in the subset of patients who were remaining on therapy for 6 or more weeks. Study C1 Study C1 was conducted in patients with anemia (hemoglobin < 11.5 g/dL for males; < 10.5 g/dL for females) with non-myeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Randomization was stratified by type of malignancy (lung vs. breast vs. other), concurrent radiation therapy planned (yes or no), and baseline hemoglobin (< 9 g/dL vs. ≥ 9 g/dL); patients were randomized to epoetin alfa 40,000 Units (n = 174) or placebo (n = 170) as a weekly subcutaneous injection commencing on the first day of the chemotherapy cycle. Ninety-one percent of patients were white, 44% were male, and the median age of patients was 66 years (range: 20 to 88 years). The proportion of patients withdrawn from the study prior to week 5 was less than 10% for placebo-treated or epoetin-treated patients. Per protocol, the last available hemoglobin values from patients who dropped out were included in the efficacy analyses. Efficacy results are shown in Table 9. Table 9. Study C1: Proportion of Patients Transfused Week 5 Through Week 16 or End of Study a Chemotherapy Regime n Epogen ( n = 174) Placebo ( n = 170) All Regimens 14% (25/174) b 28% (48/170) Regimens without cisplatin 14% (21/148) 26% (35/137) Regimens containing cisplatin 15% (4/26) 39% (13/33) a Last-known RBC transfusion status carried forward for patients who discontinued treatment. b Two-sided p < 0.001, logistic regression analysis adjusting for accrual rate and stratification variables Study C2 Study C2 was conducted in 222 patients with anemia, ages 5 to 18, receiving chemotherapy for the treatment of various childhood malignancies. Randomization was stratified by cancer type (solid tumors, Hodgkin’s disease, acute lymphocytic leukemia, vs. non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma); patients were randomized to receive epoetin alfa at 600 Units/kg maximum 40,000 Units (n = 111) or placebo (n = 111) as a weekly intravenous injection. Sixty-nine percent of patients were white, 55% were male, and the median age of patients was 12 years (range: 5 to 18 years). Two (2%) of placebo-treated patients and 3 (3%) of epoetin alfa-treated patients dropped out of the study prior to week 5. There were fewer RBC transfusions from week 5 through the end-of-study in epoetin alfa-treated patients [51% (57/111)] compared to placebo-treated patients [69% (77/111)]. There was no evidence of an improvement in health-related quality of life, including no evidence of an effect on fatigue, energy, or strength in patients receiving Epogen as compared to those receiving placebo. Pooled Analysis ( Three T imes P er W eek D osing) The results of 6 studies of similar design and that randomized 131 patients to epoetin alfa or placebo were pooled to assess the safety and effectiveness of epoetin alfa. Patients were randomized to receive epoetin alfa at 150 Units/kg (n = 63) or placebo (n = 68), subcutaneously three times per week for 12 weeks in each study. Across all studies, 72 patients were treated with concomitant non cisplatin-containing chemotherapy regimens and 59 patients were treated with concomitant cisplatin-containing chemotherapy regimens. Twelve patients (19%) in the epoetin alfa arm and 10 patients (15%) in the placebo-arm dropped out prior to week 6 and are excluded from efficacy analyses. Table 10: Proportion of Patients Transfused in the Pooled Analysis for Three Times Per Week Dosing Week 5 Through W eek 12 or End of Study a Chemotherapy Regime n Epogen Placebo All Regimens 22% (11/51) b 43% (25/58) Regimens without cisplatin 21% (6/29) 33% (11/33) Regimens containing cisplatin 23% (5/22) 56% (14/25) a Limited to patients remaining on study beyond week 6 and includes only RBC transfusions during weeks 5-12. b Two-sided p < 0.05, unadjusted 14.4 Surgery Patients The safety and efficacy of Epogen were evaluated in a placebo-controlled, double-blind study (S1) enrolling 316 patients scheduled for major, elective orthopedic hip or knee surgery who were expected to require ≥ 2 units of blood and who were not able or willing to participate in an autologous blood donation program. Patients were stratified into 1 of 3 groups based on their pretreatment hemoglobin [≤ 10 g/dL (n = 2), > 10 to ≤ 13 g/dL (n = 96), and > 13 to ≤ 15 g/dL (n = 218)] and then randomly assigned to receive 300 Units/kg Epogen, 100 Units/kg Epogen, or placebo by subcutaneous injection for 10 days before surgery, on the day of surgery, and for 4 days after surgery. All patients received oral iron and a low-dose, postoperative warfarin regimen. Treatment with Epogen 300 Units/kg significantly (p = 0.024) reduced the risk of allogeneic RBC transfusion in patients with a pretreatment hemoglobin of > 10 to ≤ 13 g/dL; 5/31 (16%) of patients treated with Epogen 300 Units/kg, 6/26 (23%) of patients treated with Epogen 100 Units/kg, and 13/29 (45%) of placebo-treated patients were transfused. There was no significant difference in the number of patients transfused between Epogen (9% 300 Units/kg, 6% 100 Units/kg) and placebo (13%) in the > 13 to ≤ 15 g/dL hemoglobin stratum. There were too few patients in the ≤ 10 g/dL group to determine if Epogen is useful in this hemoglobin strata. In the > 10 to ≤ 13 g/dL pretreatment stratum, the mean number of units transfused per Epogen-treated patient (0.45 units blood for 300 Units/kg, 0.42 units blood for 100 Units/kg) was less than the mean transfused per placebo-treated patient (1.14 units) (overall p = 0.028). In addition, mean hemoglobin, hematocrit, and reticulocyte counts increased significantly during the presurgery period in patients treated with Epogen. Epogen was also evaluated in an open-label, parallel-group study (S2) enrolling 145 patients with a pretreatment hemoglobin level of ≥ 10 to ≤ 13 g/dL who were scheduled for major orthopedic hip or knee surgery and who were not participating in an autologous program. Patients were randomly assigned to receive 1 of 2 subcutaneous dosing regimens of Epogen (600 Units/kg once weekly for 3 weeks prior to surgery and on the day of surgery, or 300 Units/kg once daily for 10 days prior to surgery, on the day of surgery, and for 4 days after surgery). All patients received oral iron and appropriate pharmacologic anticoagulation therapy. From pretreatment to presurgery, the mean increase in hemoglobin in the 600 Units/kg weekly group (1.44 g/dL) was greater than that observed in the 300 Units/kg daily group. The mean increase in absolute reticulocyte count was smaller in the weekly group (0.11 x 10 6 /mm 3 ) compared to the daily group (0.17 x 10 6 /mm 3 ). Mean hemoglobin levels were similar for the 2 treatment groups throughout the postsurgical period. The erythropoietic response observed in both treatment groups resulted in similar RBC transfusion rates [11/69 (16%) in the 600 Units/kg weekly group and 14/71 (20%) in the 300 Units/kg daily group]. The mean number of units transfused per patient was approximately 0.3 units in both treatment groups.
Clinical Studies Table
| Starting Dose (3 Times Weekly Intravenously) | Hemoglobin Increase in 2 Weeks |
| 50 Units/kg | 0.5 g/dL |
| 100 Units/kg | 0.8 g/dL |
| 150 Units/kg | 1.2 g/dL |
Geriatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use Of the 4553 patients who received Epogen in the 6 studies for treatment of anemia due to CKD not receiving dialysis, 2726 (60%) were age 65 years and over, while 1418 (31%) were 75 years and over. Of the 757 patients who received Epogen in the 3 studies of CKD patients on dialysis, 361 (47%) were age 65 years and over, while 100 (13%) were 75 years and over. No differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between geriatric and younger patients. Dose selection and adjustment for an elderly patient should be individualized to achieve and maintain the target hemoglobin [see Dosage and Administration ( 2 )]. Among 778 patients enrolled in the 3 clinical studies of Epogen for the treatment of anemia due to concomitant chemotherapy, 419 received Epogen and 359 received placebo. Of the 419 who received Epogen, 247 (59%) were age 65 years and over, while 78 (19%) were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between geriatric and younger patients. The dose requirements for Epogen in geriatric and younger patients within the 3 studies were similar. Among 1731 patients enrolled in the 6 clinical studies of Epogen for reduction of allogeneic RBC transfusions in patients undergoing elective surgery, 1085 received Epogen and 646 received placebo or standard of care treatment. Of the 1085 patients who received Epogen, 582 (54%) were age 65 years and over, while 245 (23%) were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between geriatric and younger patients. The dose requirements for Epogen in geriatric and younger patients within the 4 studies using the 3 times weekly schedule and 2 studies using the weekly schedule were similar. Insufficient numbers of patients age 65 years or older were enrolled in clinical studies of Epogen for the treatment of patients treated with zidovudine for HIV-infection to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Pediatric Use
8.4 Pediatric Use The multiple-dose vials are formulated with benzyl alcohol and are contraindicated for use in neonates and infants [see Contraindications ( 4 ) , Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 ) ] . When therapy with Epogen is needed in neonates and infants, use the single-dose vial, which is a benzyl alcohol-free formulation. Do not mix the single-dose vials with bacteriostatic saline when administering Epogen to neonates or infants because it contains benzyl alcohol [se e Dosage and Administration ( 2.6 ) ] . Serious adverse reactions including fatal reactions and the “gasping syndrome” occurred in premature neonates and infants in the neonatal intensive care unit who received drugs containing benzyl alcohol as a preservative. In these cases, benzyl alcohol dosages of 99 to 234 mg/kg/day produced high levels of benzyl alcohol and its metabolites in the blood and urine (blood levels of benzyl alcohol were 0.61 to 1.378 mmol/L). Additional adverse reactions included gradual neurological deterioration, seizures, intracranial hemorrhage, hematologic abnormalities, skin breakdown, hepatic and renal failure, hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiovascular collapse. Preterm, low birth weight infants may be more likely to develop these reactions because they may be less able to metabolize benzyl alcohol. The minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which serious adverse reactions may occur is not known [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 )] . Pediatric Patients with CKD Epogen is indicated in pediatric patients, ages 1 month to 16 years of age, for the treatment of anemia associated with CKD requiring dialysis. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients less than 1 month old have not been established [see Clinical Studies ( 14.1 )] . Use of Epogen in pediatric patients with CKD not requiring dialysis is supported by efficacy in pediatric patients requiring dialysis. The mechanism of action of Epogen is the same for these two populations. Published literature also has reported the use of Epogen in pediatric patients with CKD not requiring dialysis. Dose-dependent increases in hemoglobin and hematocrit were observed with reductions in transfusion requirements. The safety data from the pediatric studies and postmarketing reports are similar to those obtained from the studies of Epogen in adult patients with CKD [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5 ) and Adverse Reactions ( 6.1 )] . Postmarketing reports do not indicate a difference in safety profiles in pediatric patients with CKD requiring dialysis and not requiring dialysis. Pediatric Patients with Cancer on Chemotherapy Epogen is indicated in patients 5 to 18 years old for the treatment of anemia due to concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients less than 5 years of age have not been established [see Clinical Studies ( 14.3 )] . The safety data from these studies are similar to those obtained from the studies of Epogen in adult patients with cancer [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 , 5.2 ) and Adverse Reactions ( 6.1 )]. Pediatric Patients With HIV - i nfection Receiving Zidovudine Published literature has reported the use of Epogen in 20 zidovudine-treated, anemic, pediatric patients with HIV-infection, ages 8 months to 17 years, treated with 50 to 400 Units/kg subcutaneously or intravenously 2 to 3 times per week. Increases in hemoglobin levels and in reticulocyte counts and decreases in or elimination of RBC transfusions were observed. Pharmacokinetics in N eonates Limited pharmacokinetic data from a study of 7 preterm, very low birth weight neonates and 10 healthy adults given intravenous erythropoietin suggested that distribution volume was approximately 1.5 to 2 times higher in the preterm neonates than in the healthy adults, and clearance was approximately 3 times higher in the preterm neonates than in the healthy adults.
Pregnancy
8.1 Pregnancy Risk Summary Epogen from multiple-dose vials contains benzyl alcohol and is contraindicated in pregnant women [see Contraindications ( 4 )] . When therapy with Epogen is needed during pregnancy, use a benzyl alcohol-free formulation (i.e., single-dose vial). Do not mix Epogen with bacteriostatic saline when administering to pregnant women because it contains benzyl alcohol ( see Clinical Considerations ) [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1 ) ] . The limited available data on Epogen use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. In animal reproductive and developmental toxicity studies, adverse fetal effects including embryo-fetal death, skeletal anomalies, and growth defects occurred when pregnant rats received epoetin alfa at doses approximating the clinical recommended starting doses ( see Dat a) . Consider the benefits and risks of Epogen single-dose vials for the mother and possible risks to the fetus when prescribing Epogen to a pregnant woman. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. Clinical Considerations Fetal / Neonatal Adverse Reactions The multiple-dose vials of Epogen contain benzyl alcohol. The preservative benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse reactions and death when administered intravenously to neonates and infants [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 ), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4 ) ]. There is a potential for similar risks to fetuses exposed to benzyl alcohol in utero . Data Human Data There are reports of pregnant women with anemia alone or anemia associated with severe renal disease and other hematologic disorders who received Epogen. Polyhydramnios and intrauterine growth restriction were reported in women with chronic renal disease, which is associated with an increased risk for these adverse pregnancy outcomes. Due to the limited number of exposed pregnancies and multiple confounding factors (such as underlying maternal conditions, other maternal medications, and gestational timing of exposure), these published case reports and studies do not reliably estimate the frequency, presence or absence of adverse outcomes. Animal Data When rats received Epogen at doses greater than or equal to 100 Units/kg/day during mating and through early pregnancy (dosing stopped prior to organogenesis), there were slight increases in the incidences of pre- and post-implantation loss, and a decrease in live fetuses in the presence of maternal toxicity (red limbs/pinna, focal splenic capsular toxicity, increased organ weights). This animal dose level of 100 Units/kg/day may approximate the clinical recommended starting dose, depending on the treatment indication. When pregnant rats and rabbits received intravenous doses of up to 500 mg/kg/day of Epogen only during organogenesis (gestational days 7 to 17 in rats and gestational days 6 to 18 in rabbits), no teratogenic effects were observed in the offspring. The offspring (F1 generation) of the treated rats were observed postnatally; rats from the F1 generation reached maturity and were mated; no Epogen-related effects were apparent for their offspring (F2 generation fetuses). When pregnant rats received Epogen at doses of 500 Units/kg/day late in pregnancy (after the period of organogenesis from day 17 of gestation through day 21 of lactation), pups exhibited decreased number of caudal vertebrae, decreased body weight gain, and delayed appearance of abdominal hair, eyelid opening, and ossification in the presence of maternal toxicity (red limbs/pinna, increased organ weights). This animal dose level of 500 U/kg/day is approximately five times the clinical recommended starting dose depending on the patient’s treatment indication.
Use In Specific Populations
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy Risk Summary Epogen from multiple-dose vials contains benzyl alcohol and is contraindicated in pregnant women [see Contraindications ( 4 )] . When therapy with Epogen is needed during pregnancy, use a benzyl alcohol-free formulation (i.e., single-dose vial). Do not mix Epogen with bacteriostatic saline when administering to pregnant women because it contains benzyl alcohol ( see Clinical Considerations ) [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1 ) ] . The limited available data on Epogen use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. In animal reproductive and developmental toxicity studies, adverse fetal effects including embryo-fetal death, skeletal anomalies, and growth defects occurred when pregnant rats received epoetin alfa at doses approximating the clinical recommended starting doses ( see Dat a) . Consider the benefits and risks of Epogen single-dose vials for the mother and possible risks to the fetus when prescribing Epogen to a pregnant woman. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. Clinical Considerations Fetal / Neonatal Adverse Reactions The multiple-dose vials of Epogen contain benzyl alcohol. The preservative benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse reactions and death when administered intravenously to neonates and infants [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 ), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4 ) ]. There is a potential for similar risks to fetuses exposed to benzyl alcohol in utero . Data Human Data There are reports of pregnant women with anemia alone or anemia associated with severe renal disease and other hematologic disorders who received Epogen. Polyhydramnios and intrauterine growth restriction were reported in women with chronic renal disease, which is associated with an increased risk for these adverse pregnancy outcomes. Due to the limited number of exposed pregnancies and multiple confounding factors (such as underlying maternal conditions, other maternal medications, and gestational timing of exposure), these published case reports and studies do not reliably estimate the frequency, presence or absence of adverse outcomes. Animal Data When rats received Epogen at doses greater than or equal to 100 Units/kg/day during mating and through early pregnancy (dosing stopped prior to organogenesis), there were slight increases in the incidences of pre- and post-implantation loss, and a decrease in live fetuses in the presence of maternal toxicity (red limbs/pinna, focal splenic capsular toxicity, increased organ weights). This animal dose level of 100 Units/kg/day may approximate the clinical recommended starting dose, depending on the treatment indication. When pregnant rats and rabbits received intravenous doses of up to 500 mg/kg/day of Epogen only during organogenesis (gestational days 7 to 17 in rats and gestational days 6 to 18 in rabbits), no teratogenic effects were observed in the offspring. The offspring (F1 generation) of the treated rats were observed postnatally; rats from the F1 generation reached maturity and were mated; no Epogen-related effects were apparent for their offspring (F2 generation fetuses). When pregnant rats received Epogen at doses of 500 Units/kg/day late in pregnancy (after the period of organogenesis from day 17 of gestation through day 21 of lactation), pups exhibited decreased number of caudal vertebrae, decreased body weight gain, and delayed appearance of abdominal hair, eyelid opening, and ossification in the presence of maternal toxicity (red limbs/pinna, increased organ weights). This animal dose level of 500 U/kg/day is approximately five times the clinical recommended starting dose depending on the patient’s treatment indication. 8.2 Lactation Risk Summary Epogen from multiple-dose vials contains benzyl alcohol and is contraindicated in lactating women [see Contraindications ( 4 ) , Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 ) ] . Advise a lactating woman not to breastfeed for at least 2 weeks after the last dose. The preservative benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse reactions and death when administered intravenously to neonates and infants [ see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4 ) ]. There is a potential for similar risks to infants exposed to benzyl alcohol through human milk. Do not mix Epogen with bacteriostatic saline containing benzyl alcohol, if administering Epogen to a lactating woman [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1 ) ] . There is no information regarding the presence of Epogen in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, endogenous erythropoietin is present in human milk. Because many drugs are present in human milk, caution should be exercised when Epogen from single-dose vials is administered to a lactating woman. 8.4 Pediatric Use The multiple-dose vials are formulated with benzyl alcohol and are contraindicated for use in neonates and infants [see Contraindications ( 4 ) , Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 ) ] . When therapy with Epogen is needed in neonates and infants, use the single-dose vial, which is a benzyl alcohol-free formulation. Do not mix the single-dose vials with bacteriostatic saline when administering Epogen to neonates or infants because it contains benzyl alcohol [se e Dosage and Administration ( 2.6 ) ] . Serious adverse reactions including fatal reactions and the “gasping syndrome” occurred in premature neonates and infants in the neonatal intensive care unit who received drugs containing benzyl alcohol as a preservative. In these cases, benzyl alcohol dosages of 99 to 234 mg/kg/day produced high levels of benzyl alcohol and its metabolites in the blood and urine (blood levels of benzyl alcohol were 0.61 to 1.378 mmol/L). Additional adverse reactions included gradual neurological deterioration, seizures, intracranial hemorrhage, hematologic abnormalities, skin breakdown, hepatic and renal failure, hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiovascular collapse. Preterm, low birth weight infants may be more likely to develop these reactions because they may be less able to metabolize benzyl alcohol. The minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which serious adverse reactions may occur is not known [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 )] . Pediatric Patients with CKD Epogen is indicated in pediatric patients, ages 1 month to 16 years of age, for the treatment of anemia associated with CKD requiring dialysis. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients less than 1 month old have not been established [see Clinical Studies ( 14.1 )] . Use of Epogen in pediatric patients with CKD not requiring dialysis is supported by efficacy in pediatric patients requiring dialysis. The mechanism of action of Epogen is the same for these two populations. Published literature also has reported the use of Epogen in pediatric patients with CKD not requiring dialysis. Dose-dependent increases in hemoglobin and hematocrit were observed with reductions in transfusion requirements. The safety data from the pediatric studies and postmarketing reports are similar to those obtained from the studies of Epogen in adult patients with CKD [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5 ) and Adverse Reactions ( 6.1 )] . Postmarketing reports do not indicate a difference in safety profiles in pediatric patients with CKD requiring dialysis and not requiring dialysis. Pediatric Patients with Cancer on Chemotherapy Epogen is indicated in patients 5 to 18 years old for the treatment of anemia due to concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients less than 5 years of age have not been established [see Clinical Studies ( 14.3 )] . The safety data from these studies are similar to those obtained from the studies of Epogen in adult patients with cancer [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 , 5.2 ) and Adverse Reactions ( 6.1 )]. Pediatric Patients With HIV - i nfection Receiving Zidovudine Published literature has reported the use of Epogen in 20 zidovudine-treated, anemic, pediatric patients with HIV-infection, ages 8 months to 17 years, treated with 50 to 400 Units/kg subcutaneously or intravenously 2 to 3 times per week. Increases in hemoglobin levels and in reticulocyte counts and decreases in or elimination of RBC transfusions were observed. Pharmacokinetics in N eonates Limited pharmacokinetic data from a study of 7 preterm, very low birth weight neonates and 10 healthy adults given intravenous erythropoietin suggested that distribution volume was approximately 1.5 to 2 times higher in the preterm neonates than in the healthy adults, and clearance was approximately 3 times higher in the preterm neonates than in the healthy adults. 8.5 Geriatric Use Of the 4553 patients who received Epogen in the 6 studies for treatment of anemia due to CKD not receiving dialysis, 2726 (60%) were age 65 years and over, while 1418 (31%) were 75 years and over. Of the 757 patients who received Epogen in the 3 studies of CKD patients on dialysis, 361 (47%) were age 65 years and over, while 100 (13%) were 75 years and over. No differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between geriatric and younger patients. Dose selection and adjustment for an elderly patient should be individualized to achieve and maintain the target hemoglobin [see Dosage and Administration ( 2 )]. Among 778 patients enrolled in the 3 clinical studies of Epogen for the treatment of anemia due to concomitant chemotherapy, 419 received Epogen and 359 received placebo. Of the 419 who received Epogen, 247 (59%) were age 65 years and over, while 78 (19%) were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between geriatric and younger patients. The dose requirements for Epogen in geriatric and younger patients within the 3 studies were similar. Among 1731 patients enrolled in the 6 clinical studies of Epogen for reduction of allogeneic RBC transfusions in patients undergoing elective surgery, 1085 received Epogen and 646 received placebo or standard of care treatment. Of the 1085 patients who received Epogen, 582 (54%) were age 65 years and over, while 245 (23%) were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between geriatric and younger patients. The dose requirements for Epogen in geriatric and younger patients within the 4 studies using the 3 times weekly schedule and 2 studies using the weekly schedule were similar. Insufficient numbers of patients age 65 years or older were enrolled in clinical studies of Epogen for the treatment of patients treated with zidovudine for HIV-infection to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Epogen (epoetin alfa) injection is a sterile, clear, and colorless solution available as: Preservative- f ree , s ingle- d ose v ial s (in citrate-buffered formulation) : 2,000 Units/mL (NDC 55513-126-10), 3,000 Units/mL (NDC 55513-267-10), 4,000 Units/mL (NDC 55513-148-10), or 10,000 Units/mL (NDC 55513-144-10) supplied in dispensing packs containing ten 1 mL single-dose vials. Preserved, m ulti ple - dose v ial: 20,000 Units/2 mL (10,000 Units/mL) (NDC 55513-283-10) supplied in dispensing packs containing ten 2 mL multiple-dose vials. Preserved , m ulti ple- dose v ial: 20,000 Units/mL (NDC 55513-478-10) supplied in dispensing packs containing ten 1 mL multiple-dose vials. Store at 36 o F to 46 o F (2 o C to 8 o C). Do not freeze. Do not shake. Do not use Epogen that has been shaken or frozen. Store Epogen vials in the original carton until use to protect from light.
Boxed Warning
WARNING: ESAs INCREASE THE RISK OF DEATH, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION, STROKE, VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM, THROMBOSIS OF VASCULAR ACCESS AND TUMOR PROGRESSION OR RECURRENCE Chronic Kidney Disease: In controlled trials, patients experienced greater risks for death, serious adverse cardiovascular reactions, and stroke when administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to target a hemoglobin level of greater than 11 g/dL [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] . No trial has identified a hemoglobin target level, E SA dose, or dosing strategy that does not increase these risks [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.2 )] . Use the lowest Epogen dose sufficient to reduce the need for red blood cell (RBC) transfusions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] . Cancer: ESAs shortened overall survival and/or increased the risk of tumor progression or recurrence in clinical studies of patients with breast, non-small cell lung, head and neck, lymphoid, and cervical cancers [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2 )]. To decrease these risks, as well as the risk of serious cardiovascular and thromboembolic reactions, use the lowest dose needed to avoid RBC transfusions [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4 )]. Use ESAs only for anemia from myelosuppressive chemotherapy [see Indications and Usage ( 1.3 )]. ESAs are not indicated for patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy when the anticipated outcome is cure [see Indications and Usage ( 1.5 )]. Discontinue following the completion of a chemotherapy course [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4 )]. Perisurgery: Due to increased risk of Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT), DVT prophylaxis is recommended [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.5 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )]. WARNING: ESAs INCREASE THE RISK OF DEATH, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION, STROKE, VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM, THROMBOSIS OF VASCULAR ACCESS AND TUMOR PROGRESSION OR RECURRENCE See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Chronic Kidney Disease: In controlled trials, patients experienced greater risks for death, serious adverse cardiovascular reactions, and stroke when administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to target a hemoglobin level of greater than 11 g/dL ( 5.1 ). No trial has identified a hemoglobin target level, E SA dose, or dosing strategy that does not increase these risks ( 2.2 ) . Use the lowest Epogen dose sufficient to reduce the need for red blood cell (RBC) transfusions ( 5.1 ). Cancer : ESAs shortened overall survival and/or increased the risk of tumor progression or recurrence in clinical studies of patients with breast, non-small cell lung, head and neck, lymphoid, and cervical cancers ( 5.2 ). Use the lowest dose to avoid RBC transfusions ( 2.4 ). Use ESAs only for anemia from myelosuppressive chemotherapy ( 1.3 ) . ESAs are not indicated for patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy when the anticipated outcome is cure ( 1.5 ). Discontinue following the completion of a chemotherapy course ( 2.4 ). Perisurgery : Due to increased risk of deep venous thrombosis ( DVT ) , DVT prophylaxis is recommended ( 5.1 ).
Relevant Learning Zones

Supportive care in oncology from a multidisciplinary team involves caring for patients with cancer, treatment adherence and adverse effect management.
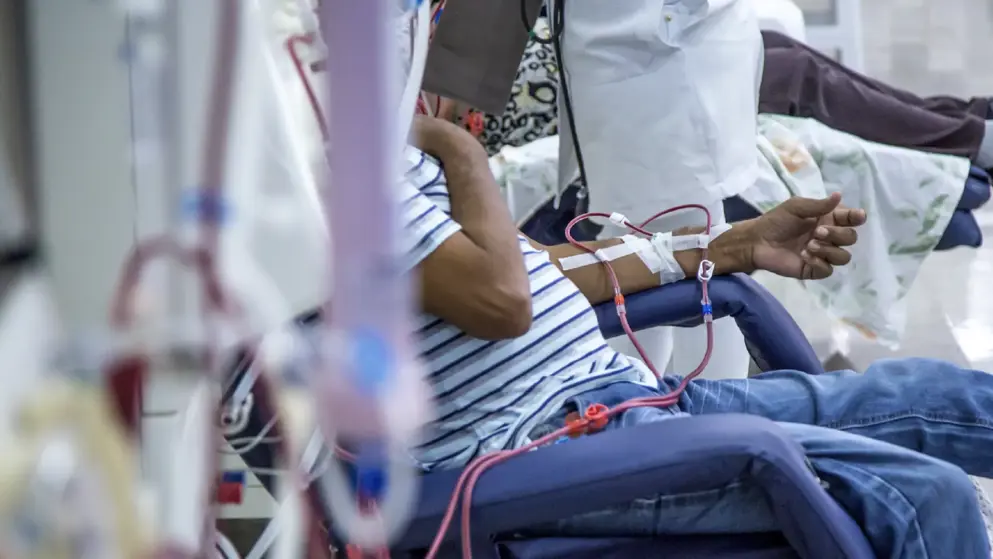
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a disease that can often lead to a need for haemodialysis and kidney transplantation. New CKD treatments are emerging which focus on delaying CKD disease progression and the need for transplantation.
Learning Zones
The Learning Zones are an educational resource for healthcare professionals that provide medical information on the epidemiology, pathophysiology and burden of disease, as well as diagnostic techniques and treatment regimens.
Disclaimer
The drug Prescribing Information (PI), including indications, contra-indications, interactions, etc, has been developed using the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) as a source (www.fda.gov).
Medthority offers the whole library of PI documents from the FDA. Medthority will not be held liable for explicit or implicit errors, or missing data.
Drugs appearing in this section are approved by the FDA. For regions outside of the United States, this content is for informational purposes only and may not be aligned with local regulatory approvals or guidance.

