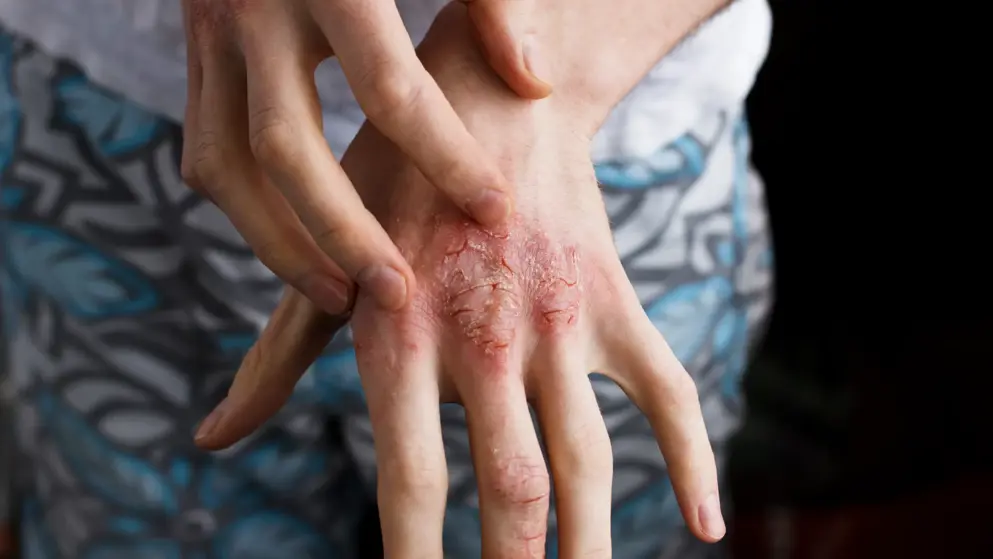
FDA OKs Nemluvio for Severe Atopic Dermatitis
Galderma announced that the FDA has approved Nemluvio (nemolizumab) for the treatment of patients 12 years and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, in combination with topical corticosteroids (TCS) and/or calcineurin inhibitors (TCI) when the disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies
This follows the recent U.S. FDA approval of Nemluvio for subcutaneous injection for the treatment of adults with prurigo nodularis in August 2024
Atopic dermatitis affects more than 230 million people worldwide, impacting approximately 7% of people in the U.S. Often reported as one of patients’ most problematic symptoms, 87% of people with atopic dermatitis say they are seeking freedom from itch, with speed of itch relief therefore also prioritized by both patients and physicians. Atopic dermatitis is also a highly heterogenous disease and can be associated with several comorbid conditions, namely mental health disorders and other autoimmune- or immune-mediated diseases. For this reason, there remains a need for more novel, effective treatment options, as while currently available treatments for atopic dermatitis may improve some signs and symptoms, many patients do not respond optimally to approved therapies and do not experience itch relief and clear skin to the same degree.
Nemluvio is the first approved monoclonal antibody that specifically targets IL-31 receptor alpha, inhibiting the signaling of IL-31. IL-31 is a neuroimmune cytokine that drives itch and is involved in inflammation and epidermal dysregulation in atopic dermatitis.-
This approval is based on positive results from the phase III ARCADIA clinical trial program which evaluated the efficacy and safety of Nemluvio in combination with background TCS, with or without TCI, versus placebo in combination with TCS, with or without TCI, in 1,728 patients aged 12 years or older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.
Results demonstrated that patients treated with Nemluvio, administered subcutaneously every four weeks in combination with TCS, with or without TCI, showed statistically significant improvements on skin clearance in both co-primary endpoints. These were clearance (0) or almost-clearance (1) of skin lesions when assessed using the investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score, and achieving a 75% reduction in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) - when compared to placebo in combination with TCS, with or without TCI, after 16 weeks of treatment
The trials also met all key secondary endpoints confirming significant responses on itch as early as Week 1, and statistically significant improvements in sleep disturbance with Nemluvio in combination with TCS, with or without TCI, when compared to placebo in combination with TCS, with or without TCI.
Overall, Nemluvio was well tolerated, and the safety profile was generally consistent between Nemluvio and placebo groups.